Having a website that doesn’t convert is a little like having a bucket with a hole in it. Do you keep filling it up while the water’s pouring out — or do you fix the hole then add water? In other words, do you channel your budget into attracting people who are “pouring” through without taking action, or do you fine-tune your website so it’s appealing enough for them to stick around?
Our recommendation? Optimize the conversion rate of your website, before you spend on increasing your traffic to it.
Here’s a web design statistic to bear in mind: you have 50 milliseconds to make a good first impression. If your site’s too slow, or unattractive, or the wording isn’t clear, they’ll bounce faster than you can say “leaky bucket”. Which is a shame, because you’ve put lots of effort into designing a beautiful product page and About Us, and people just aren’t getting to see it.
As a digital web design and conversion agency in Melbourne, Australia, we’ve been helping our customers optimize their websites for over 10 years, but it wasn’t until mid-2019 that we decided to turn the tables and take a look at our own site.
As it turned out, we had a bit of a leaky bucket situation of our own: while our traffic was good and conversions were okay, there was definitely room for improvement.
In this article, I’m going to talk a little more about conversions: what they are, why they matter, and how they help your business. I’ll then share how I made lots of little tweaks that cumulatively led to my business attracting a higher tier of customers, more inquiries, plus over $780,000 worth of new sales opportunities within the first 26 weeks of making some of those changes. Let’s get into it!
What is conversion?
Your conversion rate is a figure that represents the percentage of visitors who come to your site and take the desired action, e.g. subscribing to your newsletter, booking a demo, purchasing a product, and so on.
Conversions come in all shapes and sizes, depending on what your website does. If you sell a product, making a sale would be your primary goal (aka a macro-conversion). If you run, say, a tour company or media outlet, then subscribing or booking a consultation might be your primary goal.
If your visitor isn’t quite ready to make a purchase or book a consultation, they might take an intermediary step — like signing up to your free newsletter, or following you on social media. This is what’s known as a micro-conversion: a little step that leads towards (hopefully) a bigger one.
A quick recap
A conversion can apply to any number of actions — from making a purchase, to following on social media.
Macro-conversions are those we usually associate with sales: a phone call, an email, or a trip to the checkout. These happen when the customer has done their research and is ready to leap in with a purchase. If you picture the classic conversion funnel, they’re already at the bottom.
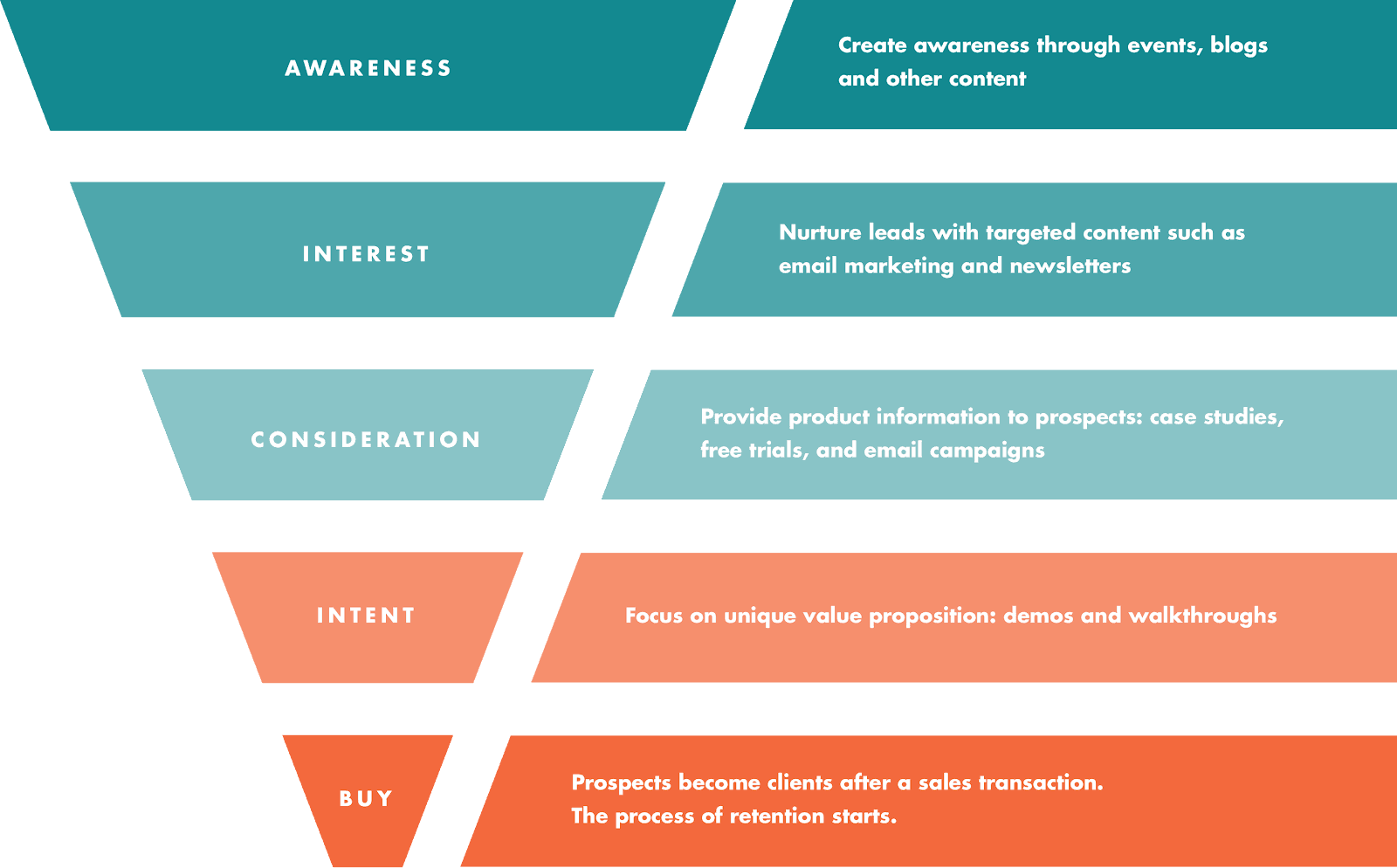
Micro-conversions, on the other hand, are small steps that lead toward a sale. They’re not the ultimate win, but they’re a step in the right direction.
Most sites and apps have multiple conversion goals, each with its own conversion rate.
Micro-conversions vs. macro-conversions: which is better?
The short answer? Both. Ideally, you want micro- and macro-conversions to be happening all the time so you have a continual flow of customers working their way through your sales funnel. If you have neither, then your website is behaving like a leaky bucket.
Here are two common issues that seem like good things, but ultimately lead to problems:
High web traffic (good thing) but no micro- or macro-conversions (bad thing — leaky bucket alert)
High web traffic (good thing) plenty of micro-conversions (good thing), but no macro conversions (bad thing)
A lot of businesses spend heaps of money making sure their employees work efficiently, but less of the budget goes into what is actually one of your best marketing tools: your website.
Spending money on marketing will always be a good thing. Getting customers to your site means more eyes on your business — but when your website doesn’t convert visitors into sales, that’s when you’re wasting your marketing dollars. When it comes to conversion rate statistics, one of the biggest eye-openers I read was this: the average user’s attention span has dropped from 12 to a mere 7 seconds. That’s how long you’ve got to impress before they bail — so you’d better make sure your website is fast, clear, and attractive.
Our problem
Our phone wasn’t ringing as much as we’d have liked, despite spending plenty of dollars on SEO and Adwords. We looked into our analytics and realized traffic wasn’t an issue: a decent number of people were visiting our site, but too few were taking action — i.e. inquiring. Here’s where some of our issues lay:
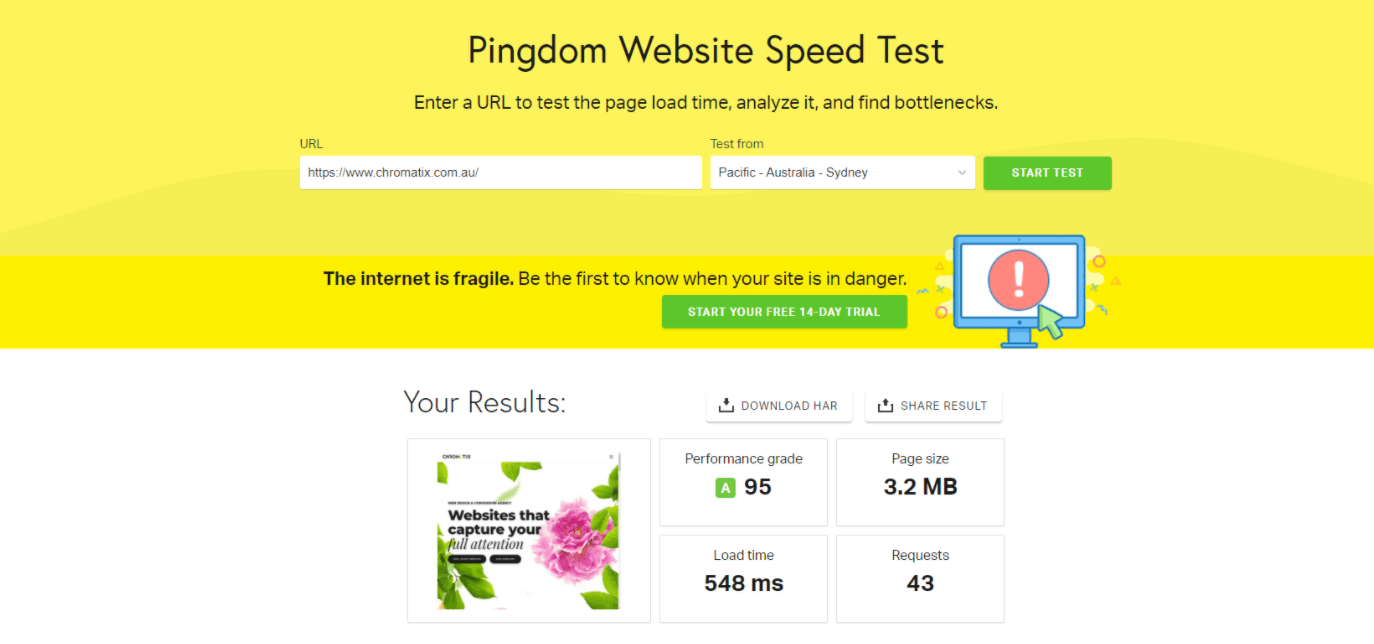
Our site wasn’t as fast as it could have been (anything with a load time of two seconds or over is considered slow. Ours was hovering around 5-6, and that was having a negative impact on conversions).
Our CTA conversions were low (people weren’t clicking — or they were dropping off because the CTA wasn’t where it needed to be).
We were relying on guesswork for some of our design decisions — which meant we had no way of measuring what worked, and what didn’t.
In general, things were good but not great. Or in other words, there was room for improvement.
What we did to fix it
Improving your site’s conversions isn’t a one-size-fits all thing — which means what works for one person might not work for you. It’s a gradual journey of trying different things out and building up successes over time. We knew this having worked on hundreds of client websites over the years, so we went into our own redesign with this in mind. Here are some of the steps we took that had an impact.
We decided to improve our site
First of all, we decided to fix our company website. This sounds like an obvious one, but how many times have you thought “I’ll do this really important thing”, then never gotten round to it. Or rushed ahead in excitement, made a few tweaks yourself, then let your efforts grind to a halt because other things took precedence?
This is an all-too-common problem when you run a business and things are just… okay. Often there’s no real drive to fix things and we fall back into doing what seems more pressing: selling, talking to customers, and running the business.
Deciding you want to improve your site’s conversions starts with a decision that involves you and everyone else in the company, and that’s what we did. We got the design and analytics experts involved. We invested time and money into the project, which made it feel substantial. We even made EDMs to announce the site launch (like the one below) to let everyone know what we’d been up to. In short, we made it feel like an event.

We got to know our users
There are many different types of user: some are ready to buy, some are just doing some window shopping. Knowing what type of person visits your site will help you create something that caters to their needs.
We looked at our analytics data and discovered visitors to our site were a bit of both, but tended to be more ready to buy than not. This meant we needed to focus on getting macro-conversions — in other words, make our site geared towards sales — while not overlooking the visitors doing some initial research. For those users, we implemented a blog as a way to improve our SEO, educate leads, and build up our reputation.
User insight can also help you shape the feel of your site. We discovered that the marketing managers we were targeting at the time were predominantly women, and that certain images and colours resonated better among that specific demographic. We didn’t go for the (obvious pictures of the team or our offices), instead relying on data and the psychology of attraction to delve into the mind of the users.
 We improved site speed
We improved site speed
Sending visitors to good sites with bad speeds erodes trust and sends them running. Multiple studies show that site speed matters when it comes to conversion rates. It’s one of the top SEO ranking factors, and a big factor when it comes to user experience: pages that load in under a second convert around 2.5 times higher than pages taking five seconds or more.
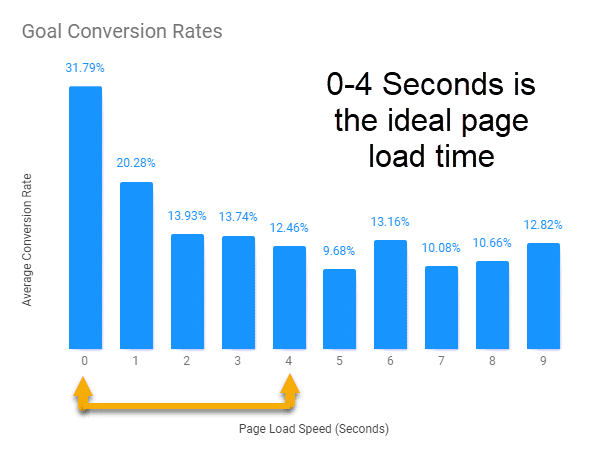
We built our website for speed. Moz has a great guide on page speed best practices, and from that list, we did the following things:
We optimized images.
We managed our own caching.
We compressed our files.
We improved page load times (Moz has another great article about how to speed up time to first Byte). A good web page load time is considered to be anything under two seconds — which we achieved.
In addition, we also customized our own hosting to make our site faster.
We introduced more tracking
As well as making our site faster, we introduced a lot more tracking. That allowed us to refine our content, our messaging, the structure of the site, and so on, which continually adds to the conversion.
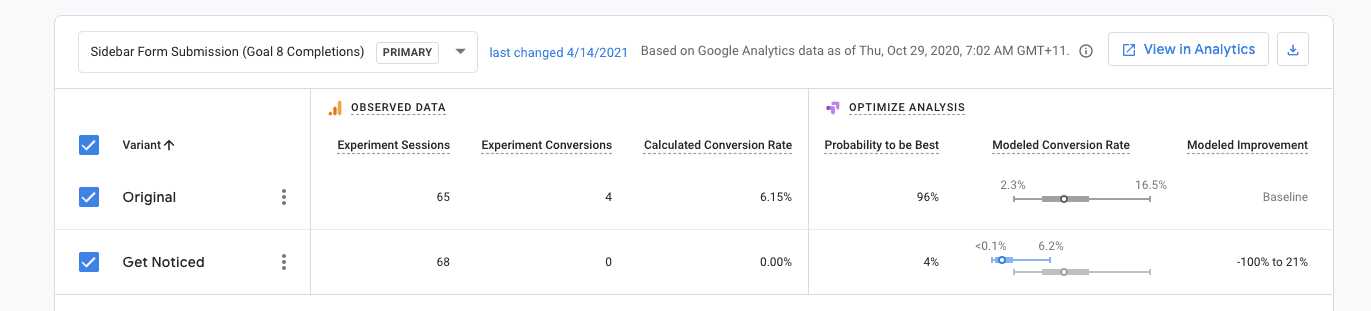
We used Google Optimize to run A/B tests across a variety of things to understand how people interacted with our site. Here are some of the tweaks we made that had a positive impact:
Social proofing can be a really effective tool if used correctly, so we added some stats to our landing page copy.
Google Analytics showed us visitors were reaching certain pages and not knowing quite where to go next, so we added CTAs that used active language. So instead of saying, “If you’d like to find out more, let us know”, we said “Get a quote”, along with two options for getting in touch.
We spent an entire month testing four words on our homepage. We actually failed (the words didn’t have a positive impact), but it allowed us to test our hypothesis. We did small tweaks and tests like this all over the site.
We used heat mapping to see where visitors were clicking, and which words caught their eye. With this data, we knew where to place buttons and key messaging.
We looked into user behavior
Understanding your visitor is always a good place to start, and there are two ways to go about this:
Quantitative research (numbers and data-based research)
Qualitative research (people-based research)
We did a mixture of both.
For the quantitative research, we used Google Analytics, Google Optimize, and Hotjar to get an in-depth, numbers-based look at how people were interacting with our site.
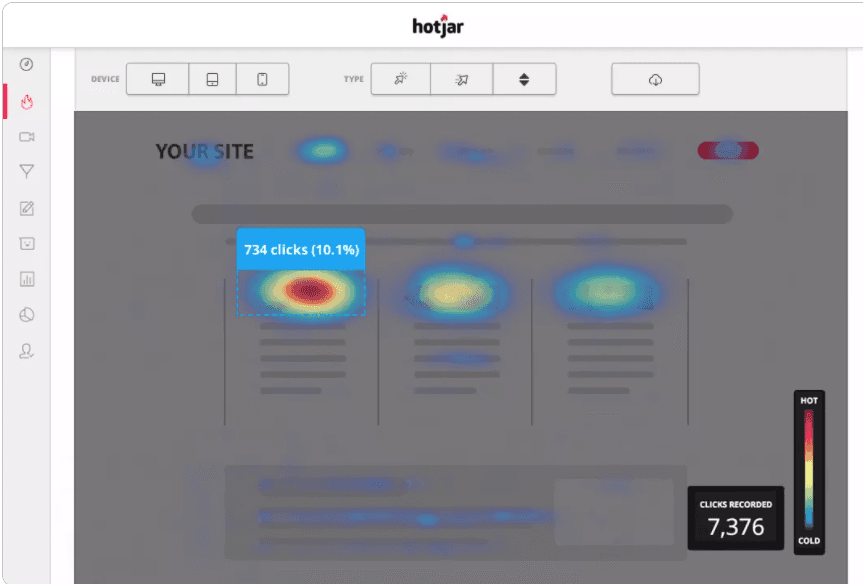
Heat-mapping software shows how people click and scroll through a page. Hot spots indicate places where people naturally gravitate.
We could see where people were coming into our site (which pages they landed on first), what channel brought them there, which features they were engaging with, how long they spent on each page, and where they abandoned the site.
For the qualitative research, we focused primarily on interviews.
We asked customers what they thought about certain CTAs (whether they worked or not, and why).
We made messaging changes and asked customers and suppliers whether they made sense.
We invited a psychologist into the office and asked them what they thought about our design.
What we learned
We found out our design was good, but our CTAs weren’t quite hitting the mark. For example, one CTA only gave the reader the option to call. But, as one of our interviewees pointed out, not everyone likes using the phone — so we added an email address.
We were intentional but ad hoc about our asking process. This worked for us — but you might want to be a bit more formal about your approach (Moz has a great practical guide to conducting qualitative usability testing if you’re after a more in-depth look).
The results
Combined, these minor tweaks had a mighty impact. There’s a big difference in how our site looks and how we rank. The bottom line: after the rebuild, we got more work, and the business did much better. Here are some of the gains we’ve seen over the past two years.
Our dwell time increased by 73%, going from 1.5 to 2.5 minutes.
We received four-times more inquiries by email and phone.
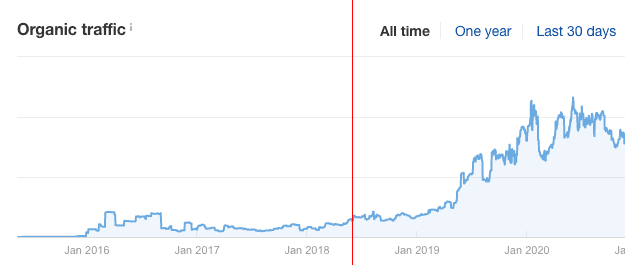
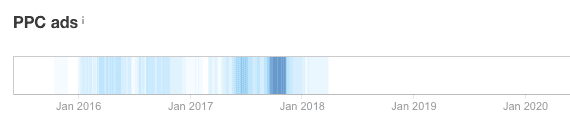
Our organic traffic increased despite us not channeling more funds into PPC ads.
We also realized our clients were bigger, paying on average 2.5 times more for jobs: in mid-2018, our average cost-per-job was $8,000. Now, it’s $17,000.
Our client brand names became more recognizable, household names — including two of Australia’s top universities, and a well-known manufacturing/production brand.
Within the first 26 weeks, we got over $770,000 worth of sales opportunities (if we’d accepted every job that came our way).
Our prospects began asking to work with us, rather than us having to persuade them to give us the business.
We started getting higher quality inquiries — warmer leads who had more intent to buy.
Some practical changes you can make to improve your website conversions
When it comes to website changes, it’s important to remember that what works for one person might not work for you.
We’ve used site speed boosters for our clients before and gotten really great results. At other times, we’ve tried it and it just broke the website. This is why it’s so important to measure as you go, use what works for your individual needs, and remember that “failures” are just as helpful as wins.
Below are some tips — some of which we did on our own site, others are things we’ve done for others.
Tip number 1: Get stronger hosting that allows you to consider things like CDNs. Hiring a developer should always be your top choice, but it’s not always possible to have that luxury. In this instance, we recommend considering CDNs, and depending on the build of your site, paying for tools like NitroPack which can help with caching and compression for faster site speeds.
Tip number 2: Focus your time. Identify top landing pages with Moz Pro and channel your efforts in these places as a priority. Use the 80/20 principle and put your attention on the 20% that gets you 80% of your success.
Tip number 3: Run A/B tests using Google Optimize to test various hypotheses and ideas (Moz has a really handy guide for running split tests using Google). Don’t be afraid of the results — failures can help confirm that what you are currently doing right. You can also access some in-depth data about your site’s performance in Google Lighthouse.
Tip number 4: Trial various messages in Google Ads (as a way of testing targeted messaging). Google provides many keyword suggestions on trending words and phrases that are worth considering.
Tip number 5: Combine qualitative and quantitative research to get to know how your users interact with your site — and keep testing on an ongoing basis.
Tip number 6: Don’t get too hung up on charts going up, or figures turning orange: do what works for you. If adding a video to your homepage slows it down a little but has an overall positive effect on your conversion, then it’s worth the tradeoff.
Tip number 7: Prioritize the needs of your target customers and focus every build and design choice around them.
Recommended tools
Nitropack: speed up your site if you’ve not built it for speed from the beginning.
Google Optimize: run A/B tests
HotJar: see how people use your site via heat mapping and behaviour analytics.
Pingdom / GTMetrix: measure site speed (both is better if you want to make sure you meet everyone’s requirements).
Google Analytics: find drop-off points, track conversion, A/B test, set goals.
Qualaroo: poll your visitors while they are on your site with a popup window.
Google Consumer Surveys: create a survey, Google recruits the participants and provides results and analysis.
Moz Pro: Identify top landing pages when you connect this tool to your Google Analytics profile to create custom reports.
How to keep your conversion rates high
Treat your website like your car. Regular little tweaks to keep it purring, occasional deeper inspections to make sure there are no problems lurking just out of sight. Here’s what we do:
We look at Google Analytics monthly. It helps to understand what’s working, and what’s not.
We use goal tracking in GA to keep things moving in the right direction.
We use Pingdom’s free service to monitor the availability and response time of our site.
We regularly ask people what they think about the site and its messaging (keeping the qualitative research coming in).
Conclusion
Spending money on marketing is a good thing, but when you don’t have a good conversion rate, that’s when your website’s behaving like a leaky bucket. Your website is one of your strongest sales tools, so it really does pay to make sure it’s working at peak performance.
I’ve shared a few of my favorite tools and techniques, but above all, my one bit of advice is to consider your own requirements. You can improve your site speed if you remove all tags and keep it plain. But that’s not what you want: it’s finding the balance between creativity and performance, and that will always depend on what’s important.
For us as a design agency, we need a site that’s beautiful and creative. Yes, having a moving background on our homepage slows it down a little bit, but it improves our conversions overall.
The bottom line: Consider your unique users, and make sure your website is in line with the goals of whoever you’re speaking with.
We can do all we want to please Google, but when it comes to sales and leads, it means more to have a higher converting and more effective website. We did well in inquiries (actual phone calls and email leads) despite a rapid increase in site performance requirements from Google. This only comes down to one thing: having a site customer conversion framework that’s effective.